| [1] Jin H,Xia B,Yu N,et al.The effects of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell arterial perfusion on vascular repair and angiogenesis in osteonecrosis of the femoral head in dogs. Int Orthop. 2012;36(12): 2589-2596.
[2] Aruwajoye OO, Patel MK, Allen MR, et al. Microcrack density and nanomechanical properties in the subchondral region of the immature piglet femoral head following ischemic osteonecrosis. Bone. 2013; 52(2): 632-639.
[3] Hu MF, Zhou XC, Shan LT, et al. Effects of Yougui recipe on the behavioral changes in rat of steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head.Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2013;26(1): 50-53.
[4] Chen ST, Zhang WP, Liu CA, et al. Experimental study on vascular bundle implantation combined with cellular transplantation in treating rabbit femoral head necrosis. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2013;26(3): 223-226.
[5] Okazaki S, Nagoya S, Tateda K, et al. Experimental rat model for alcohol-induced Osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Int J Exp Pathol. 2013;94(5):312-319.
[6] 李鸿帅,张长青.股骨头坏死动物模型研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2006, 27(3):173-175.
[7] 关俊杰,张长青.股骨头坏死动物模型研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2011,33(1):60-63.
[8] 赵凤朝,郭开今,李子荣.骨髓水肿综合征与股骨头缺血性坏死[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2011,25(4):408-411.
[9] 石少辉,李子荣,王佰亮,等.非创伤性股骨头坏死体积与坏死指数及角度相关性分析[J].中华全科医师杂志, 2009, 8(1):27-30.
[10] 鲁超,刘洪智,刘道兵,等.股骨头坏死病灶分布规律探讨[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(5):396-400.
[11] 孙泓泓,李艳捧,李兴华,等.股骨头坏死塌陷前期髋关节软骨的MRI研究[J].实用放射学杂志,2013,29(11): 1818-1822.
[12] 王程,徐小龙,袁雪凌,等.人股骨头坏死微观结构及成骨、破骨细胞活性的区域性分布特征[J].中华骨科杂志,2014, 34(4):417-424.
[13] 崔永锋,肖鲁伟,韩凤岳,等.股骨头坏死特殊病理结构的观察及其临床意义[C].2009年全国骨与关节损伤新技术研讨会论文集,2009:300-303.
[14] 黄振国,张雪哲,任安,等.股骨头缺血坏死大体标本病理与CT对照研究[J].临床放射学杂志,2012,31(7):1041-1044.
[15] 雷新玮,展影,屈瑾,等.非创伤性股骨头缺血性坏死塌陷预测的MRI研究[J].中华放射学杂志,2013,47(6):529-533.
[16] 李军伟,韩文龙,汝强,等.股骨头坏死塌陷后软骨下骨的组织学观察[J].中华实验外科杂志,2014,31(1):198-199.
[17] 崔永锋,王利明,肖鲁伟,等.股骨头坏死修复过程中断的原因分析[J].中华中医药杂志,2009,24(11):1473-1476.
[18] 魏秋实,何伟.有限元分析在股骨头坏死领域中的应用研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010,18(19):1611-1614.
[19] 陈培清.负重时机对股骨颈骨折骨愈合后股骨头坏死的影响[J].吉林医学, 2013,34(16): 3146-3147.
[20] 吴宏燕. 超声电导治疗股骨头坏死的临床研究[J].中国保健营养,2013,23(3):1563-1563.
[21] Aaron RK,Lennox D,Bunce GE, et al. A comparison of core decompression and pulsing electromagnetic fields. Clin Orthop. 1989;(249):209-218.
[22] 曹利敏,方琴,顾惠珍,等. 高压氧治疗股骨头坏死的疗效观察[J].中国现代医生,2013,51(8):141-142.
[23] 陈兴灿,刘淼,何东,等. 经皮置管术介入治疗成人股骨头坏死的疗效评价[J].中华医学杂志, 2013,93(23): 1811-1814.
[24] 暴淑英,赵庆国,毕黎琦.激素性股骨头坏死早期细胞凋亡相关基因表达及阿仑磷酸钠的干预[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(46):202-204.
[25] 高吉建,李彪,龚跃昆.激素性股骨头坏死与他汀类药物的修复治疗作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(43):108-110.
[26] 孙光伟,韩树峰,王涛.低分子肝素钙预防激素性股骨头坏死的实验研究[J].中国医疗前沿,2010,5(20):88-90.
[27] 张桐,王义生,李浩,等. 粗通道髓芯减压术治疗早期股骨头坏死的中期疗效分析[J].中国实用医刊, 2013,40(11): 25-26.
[28] 何伟,庞智晖.基于三维重建和有限元分析的股骨头坏死围塌陷期保髋新技术的临床应用[J].中华关节外科杂志, 2013,7(3):301-308.
[29] 姬树青,闻志强.髓心减压加打压植骨术后再次减压法治疗早期股骨头坏死[J].医学理论与实践, 2013,26(15): 1976-1978.
[30] Ogden JA,Alvarez RG.Shock wave the rapy in musculoskeletal disorders. Clin Orthop. 2011;357(1): 22-40.
[31] 宁杰辉,唐凯,罗伟雄.全髋关节置换术治疗创伤性股骨头坏死的临床疗效分析[J].中国保健营养,2012,2(8): 29-30.
[32] 胥少汀,葛宝丰,徐印坎.实用骨科学[M].4 版.北京人民军医出版社,2012:1857-1863.
[33] Zhang Y,Li L,Shi ZJ,et al.Porous tantalum rod implant is an effective and safe choice for early-stage femoral head necrosis:a meta-analysis of clinical trials.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2013;23(2):211-217.
[34] 康立新,温冰涛,王洪彬. 多孔金属钽棒治疗早期股骨头坏死的近期疗效观察[J].临床骨科杂志,2011,14(1): 25-28.
[35] 张颖,刘又文,魏秋实,等.AVN 钽棒置入与带旋髂深血管蒂髂骨瓣移植治疗股骨头坏死的早期疗效对比[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(15):1311-1315.
[36] Liu WG, Wang SJ, Yin QF, et al. Biomechanical supporting effect of tantalum rods for the femoral head with various sized lesions:a finite-element analysis. Chin Med J (Engl). 2012;125(22):4061-4065.
[37] Breer S, Hahn M, Kendoff D, et al. Histological ex vivo analysis of retrieved human tantalum augmentations. Int Orthop. 2012;36(11):2269-2274.
[38] Varitimidis SE,Dimitroulias AP,Karachalios TS,et al. Outcome after tantalum rod implantation for treatment of femoral head osteonecrosis: 26 hips followed for an average of 3 years. Acta Orthop. 2009;80(1): 20-25.
[39] 宋建治,肖少雄,徐礼森.多孔钽棒植入联合外周血干细胞移植治疗早期股骨头坏死的临床效果观察[J].中国综合临床,2013,29(7):757-759.
[40] 庞智晖,何伟,欧志学,等.钽棒治疗早期股骨头坏死失败原因分析与对策[J].广东医学,2012,33(1):88-91.
[41] Floerkemeier T,Thorey F,Daentzer D,et al. Clinical and radiological outcome of the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head using the osteonecrosis intervention implant. Int Orthop. 2011;35(4):489-495.
[42] Lee MS, Tai CL, Senan V. The effect of necrotic lesion size and rotational degree on the stress reduction in transtrochanteric rotational osteotomy for femoral head osteonecrosis-a three-dimensional finite-element simulation. Clin Biomech. 2006;21:969-976. |
.jpg)
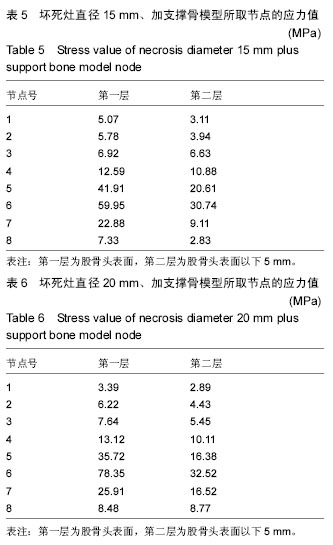
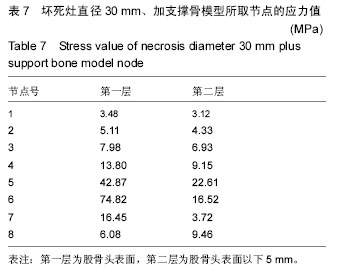
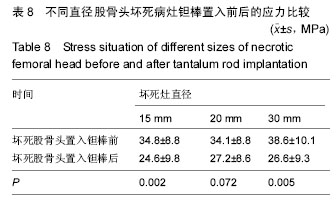
.jpg)
.jpg)